
Here’s our guide to the current ratings of commonly-used domestic appliances. Alternating current (AC) is used to supply things like houses, buildings and mains connected appliances.
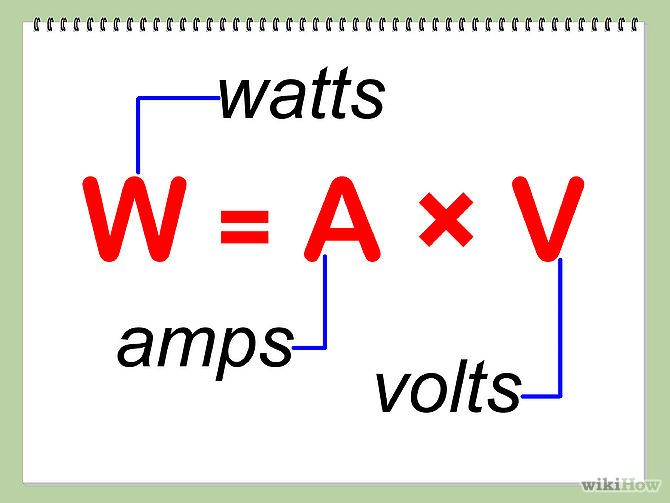
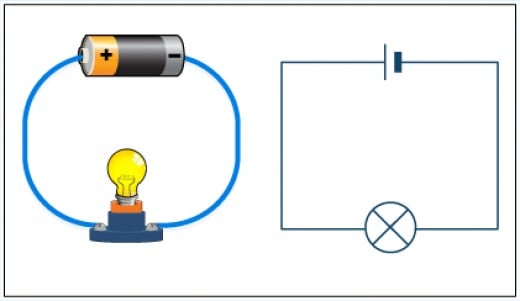
However, in alternating current (AC) the electric current changes direction at 50 times per second (50 Hz or hertz) in the UK supply.Īn example of direct current would be a battery powered torch. For direct current (DC) the electric current flows only in one direction. The labels ‘AC’ and ‘DC’ are used to describe the types of current flow in a circuit. In terms of the hosepipe example, this would refer to the amount of water being released. The higher the wattage is, the more power and output from the appliance. WattsĪmps multiplied by Volts equals Watts, which is the measurement used to determine the amount of energy. Plugging in an appliance which has a higher voltage than the socket accepts, will. In keeping with the earlier example, you could think of volts as the water pressure in the hosepipe, which makes the water flow. For example, 230V is a bigger voltage than 12V. Volts are the measurement used to determine how much force is needed to cause the electric current to flow. The more water flowing through the hosepipe, the stronger the current is. You should think of electric current as the flow of water through a hosepipe.
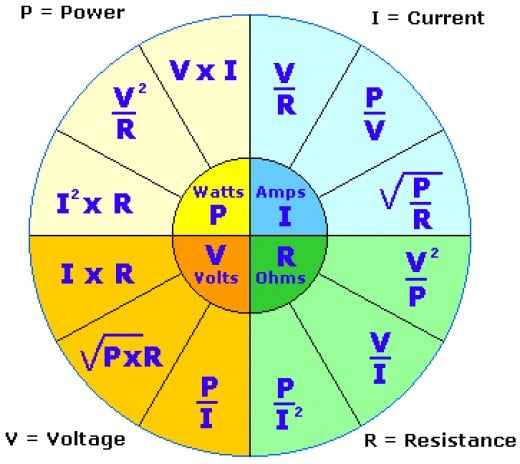
If you have a 100 amp circuit, 1 volt is equal to 100 watts. Amps x Volts = WattsĪmps measure the flow of electricity as an electric current. If you have a 1 amp circuit, 1 volt is equal to 1 watt. Amps to Watts FormulaĪlternatively to using the calculator, here are some basic equations which allow you to calculate the missing information on your own.
WATT AMP TO VOLT HOW TO
Question: 600W are being sent at 120V.Find out how to convert Watts to Amps here or how to calculate Ohm's Law here. Let's go through some examples to help nail the conversion process. Advertisements Watts to amps conversion examples Power supplied to homes and businesses uses AC supply. In Europe, the UK, East Japan and most of Australia, South America, Africa andĪsia, the current changes direction 50 times per second, which is 50Hz. In Northern America and Western Japan, this usually happens 60 times per second, or 60Hz / hertz. A flashlight with a battery uses a direct current.ĪC stands for alternating current, when the current periodically changes direction. North American homes typically use 120V for their electrical supply, whilst 230V is common acrossĭC stands for direct current, when the current flows in one single direction. When sunlight hits a solar panel, voltage and current are produced. In the hose analogy, the volts would be the water pressure. This work can be measured in Watts and is equal to Volts times Amps (Watts Volts x Amps). They measure the force required to make the electrical current (amps) flow. It uses increased water volume and higher water pressure the same applies to the wattage if amps and volts are increased. A water wheel would turn faster and longer, generating more energy if Multiplying amps (water volume) by volts (water pressure) gives you the wattage (the resulting power or energy). Watts represent the amount of energy produced by the amps and volts working together. In this analogy, the quantity (volume) of water would be the amps. It can be helpful to imagine electrical current as water in a hose. What are amps?Īmps are amperes, a unit which measures electrical current.
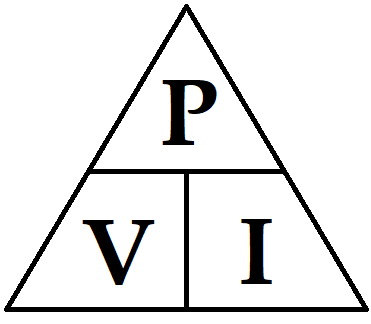
To help understand the conversion of watts to amps, let's go through what each of these units represent. When calculating power from these three units, all you need to do is multiply volts by amps and divide that number by 1000 (amps x volts 1000 watts). Advertisements Understanding watts, amps and volts


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
